下面大家将会看到的是一个极其简单而又极其复杂的“迷宫”,这无疑是我在本年度见到的最变态的谜题:从左边入口处的 2011 进去,在迷宫里转悠,最后变成 2012 从右边出来。你可以在迷宫里转圈,可以重复之前走过的路,但不能往回退着走。
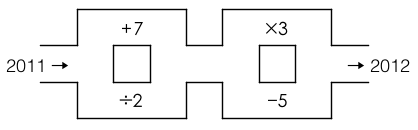
Start at 2011. By moving through the maze and doing any arithmetic operations you encounter, exit the maze with a result of 2012. You may pass through an operation several times, but not twice in a row.
原题和答案在这里:http://www2.stetson.edu/~efriedma/holiday/2011/index.html
在网上找了两个python程序。
程序一:
plus7,div2,mul3,min5=(‘+ 7′,’/ 2′,’* 3′,’- 5′)
left,middle,right=range(3)
class node:
pre_node=None
pre_opr=None
pre_pos=None
this_node=None
def __init__(self,value,opr,pos):
self.value=value
self.opr=opr
self.pos=pos
def hash(self):
return self.value*157+ord(self.opr[0])*3+self.pos
def next(self):
list=self._next()
for child in list:
child.pre_node=self.this_node
child.pre_opr=self.opr
child.pre_pos=self.pos
return list
def _next(self):
if self.opr==plus7:
child_var=self.value+7
if self.pos==left:
return node(child_var,div2,middle),node(child_var,mul3,middle),node(child_var,min5,middle)
elif self.pos==middle:
return node(child_var,div2,left),
elif self.opr==div2:
if self.value&1:
return tuple()
child_var=int(self.value)//2
if self.pos==left:
return node(child_var,plus7,middle),node(child_var,mul3,middle),node(child_var,min5,middle)
elif self.pos==middle:
return node(child_var,plus7,left),
elif self.opr==mul3:
child_var=int(self.value*3)
if self.pos==middle:
return node(child_var,min5,right),
elif self.pos==right:
return node(child_var,plus7,middle),node(child_var,div2,middle),node(child_var,min5,middle)
elif self.opr==min5:
child_var=self.value-5
if self.pos==middle:
return node(child_var,mul3,right),
elif self.pos==right:
return node(child_var,plus7,middle),node(child_var,div2,middle),node(child_var,mul3,middle)
node1=node(2011,plus7,left)
tree=[node1,]
hashlist=set([node1.hash(),])
i=0
while not (tree[i].pos==right and tree[i].value==2012):
tree[i].this_node=i
result=tree[i].next()
for item in result:
hashitem=item.hash()
if hashitem in hashlist:
continue
else:
tree.append(item)
hashlist.add(hashitem)
i+=1
#if i%100==0:
# print(i,tree[i].pos,tree[i].value)
print(‘Tried’,i,’times!’)
list=[]
while tree[i].pre_node:
list.append(i)
i=tree[i].pre_node
list.append(0)
list.reverse()
for i in range(len(list)-1):
print(tree[list[i]].value,tree[list[i]].opr,’=',tree[list[i+1]].value)
程序二:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
todo=[(2011,1,'+7',[])]
state=0
while(todo):
newtodo=[]
for num, state, cmd, history in todo:
# print num, state, cmd, history
history=list(history)
if cmd==’+7′:
history.append(‘+7′)
num+=7
elif cmd==’/2′:
history.append(‘/2′)
num/=2
elif cmd==’-5′:
history.append(‘-5′)
num-=5
else:
history.append(‘*3′)
num*=3
if num==2012:
print history
sys.exit(0)
if state==0:
if cmd==’+7′:
if(num%2==0):
newtodo.append((num,1,’/2′,history))
else:
newtodo.append((num,1,’+7′, history))
elif state==1:
if cmd==’+7′:
if(num%2==0):
newtodo.append((num,0,’/2′,history))
newtodo.append((num,2,’*3′,history))
newtodo.append((num,2,’-5′,history))
elif cmd==’/2′:
newtodo.append((num,0,’+7′,history))
newtodo.append((num,2,’*3′,history))
newtodo.append((num,2,’-5′,history))
elif cmd==’*3′:
newtodo.append((num,0,’+7′,history))
if(num%2==0):
newtodo.append((num,0,’/2′,history))
newtodo.append((num,2,’-5′,history))
else:
newtodo.append((num,0,’+7′,history))
if(num%2==0):
newtodo.append((num,0,’/2′,history))
newtodo.append((num,2,’*3′,history))
elif state==2:
if cmd==’*3′:
newtodo.append((num,1,’-5′,history))
else:
newtodo.append((num,1,’*3′,history))
todo=newtodo
我自己也写了个Python版本,用递归来实现:
#encoding=utf-8
table = ['+', '*', '/', '-']
hasmethod = 0
def calc(method, cursum, curmethods, leftright):
global hasmethod
desmethod = []
if hasmethod:
return
if method == ‘+’:
cursum += 7
curmethods += ‘+’
if cursum % 2 == 0:
desmethod.append(‘/’)
if leftright == ‘r’:
desmethod.append(‘*’)
desmethod.append(‘-’)
elif method == ‘*’:
cursum *= 3
curmethods += ‘*’
if leftright == ‘l’:
if cursum % 2 == 0:
desmethod.append(‘/’)
desmethod.append(‘+’)
desmethod.append(‘-’)
elif method == ‘-’:
cursum -= 5
curmethods += ‘-’
if leftright == ‘l’:
if cursum % 2 == 0:
desmethod.append(‘/’)
desmethod.append(‘+’)
desmethod.append(‘*’)
elif method == ‘/’:
cursum /= 2
curmethods += ‘/’
desmethod.append(‘+’)
if leftright == ‘r’:
desmethod.append(‘*’)
desmethod.append(‘-’)
if cursum == 2012:
ensuremethod(curmethods)
curmethods = curmethods.replace(‘+’, ‘+7 ‘)
curmethods = curmethods.replace(‘-’, ‘-5 ‘)
curmethods = curmethods.replace(‘*’, ‘*3 ‘)
curmethods = curmethods.replace(‘/’, ‘/2 ‘)
print curmethods
hasmethod = 1
elif len(curmethods) < 30: #防止递归调用层次过深
for m in desmethod:
curleftright = leftright
#控制方向,从左进还是从右进
if (m in ['+', '/'] and method in ['+', '/']) or (m in ['*', '-'] and method in ['*', '-']):
curleftright = ‘r’ if leftright == ‘l’ else ‘l’
calc(m, cursum, curmethods, curleftright)
def ensuremethod(methodstr):
print methodstr
print len(methodstr)
s = 2011
str0 = ”
for i in methodstr:
strs = str(s)
if i == ‘+’:
s += 7
str0 = ‘+7′
elif i == ‘-’:
s -= 5
str0 = ‘-5′
elif i == ‘*’:
s *= 3
str0 = ‘*3′
elif i == ‘/’:
s /= 2
str0 = ‘/2′
print ‘%s%s=%d’ % (strs, str0, s)
print s
hasmethod = 0
calc(‘+’, 2011, ”, ‘r’)